If you notice a facial mass or lesion on your child, it’s important to observe it carefully and document any changes. This blog will guide you on what to do if your child has a facial mass or lesion, what steps to take, when to seek medical advice, and what types of lesions are common in children.
Key Takeaways
- Facial masses in children range from benign to serious conditions, requiring careful observation and often medical intervention for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Parents should systematically monitor the size, shape, color, and any changes in their child’s facial mass or lesion, documenting symptoms for healthcare providers to aid in diagnosis.
- Treatment options vary from observation and medication to surgical removal, depending on the nature and severity of the mass or lesion.
Understanding Facial Masses and Lesions in Children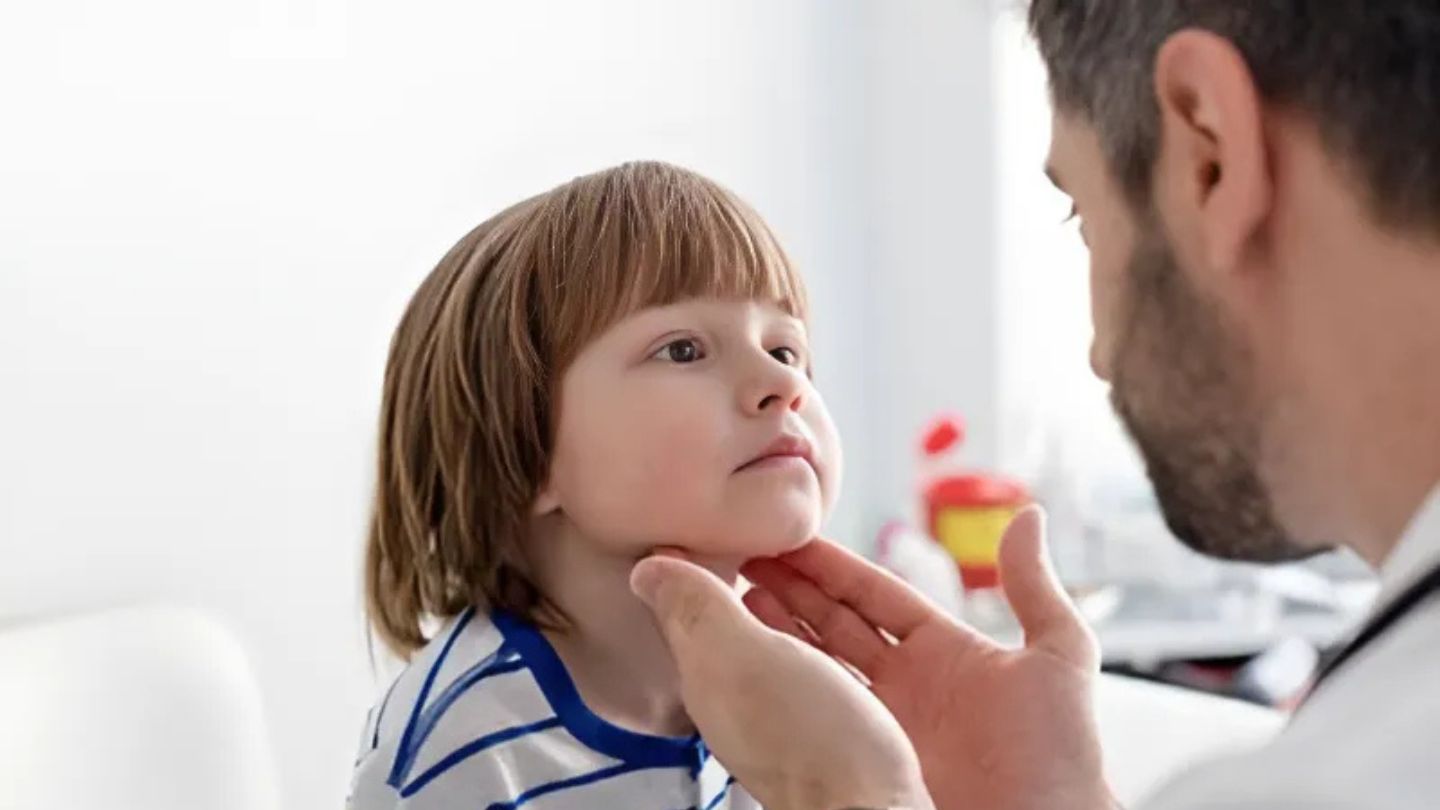
Facial masses in children can encompass a broad spectrum of conditions, ranging from benign skin growths to more serious concerns like congenital lesions and vascular anomalies. The majority of these masses are benign, meaning they are not cancerous, but their presence still necessitates careful observation and sometimes medical intervention. These facial masses can arise from various causes, including infections, congenital conditions, and even neoplastic growths. Recognizing the type of mass can significantly influence the treatment approach and outcomes, making early detection crucial.
Pediatricians and specialists play a pivotal role in identifying and managing these conditions, guiding families through the often complex landscape of diagnosis and treatment options.
Parents should stay calm and gather detailed information about the mass or lesion before consulting a healthcare provider. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions and support their child’s health.
Initial Steps for Concerned Parents
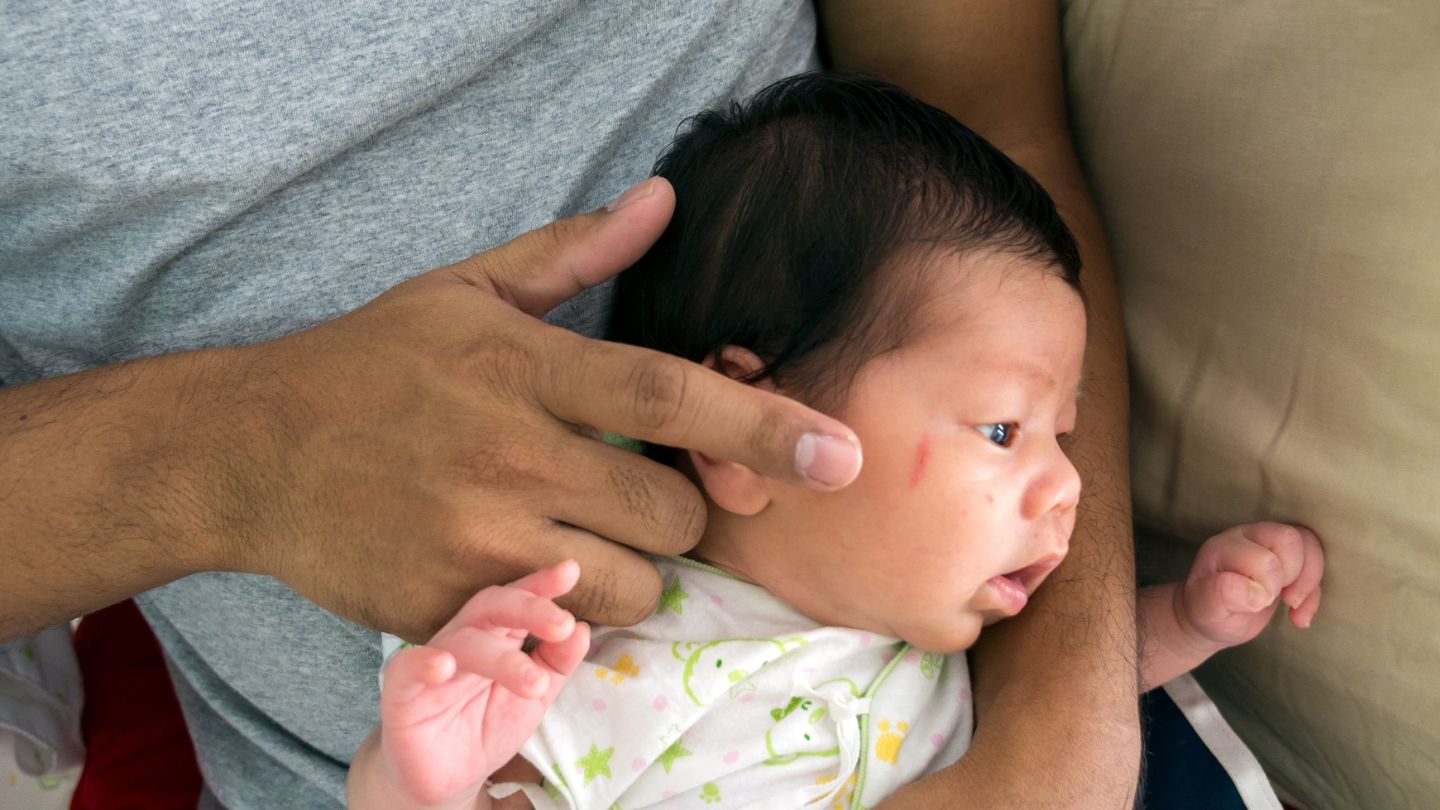
When you first notice a facial mass or lesion on your child, it’s natural to feel a surge of worry. However, taking systematic steps can help in accurately assessing the situation and determining the best course of action. Initially, parents should:
- Closely monitor the size of the facial mass or lesion over time.
- Observe the shape of the mass or lesion.
- Note the color of the mass or lesion.
- Watch for any changes in the mass or lesion over time.
This observation is critical, as it provides valuable information about the nature of the mass and can indicate whether it is benign or requires further attention.
Keeping a detailed record of any symptoms, such as pain, discomfort, or changes in the child’s health or behavior, can be immensely helpful. Documenting these symptoms can provide healthcare providers with critical insights, aiding them in making an accurate diagnosis and recommending appropriate treatment.
If the mass grows rapidly, bleed easily, or causes other concerns, prompt consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial. Early medical advice can prevent complications and ensure timely, effective care for your child.
Observe the Mass or Lesion
Tracking the characteristics of the mass or lesion helps in understanding its nature. Parents should note:
- The size of any lesions or masses on their child’s body
- The shape of any lesions or masses
- The color of any lesions or masses
- Any changes in texture or color
Such changes should be closely monitored, as they can provide critical clues about the mass’s progression and whether it might require medical attention.
Document Symptoms
Keeping a record of symptoms like pain, discomfort, or unusual behavior is crucial for assessment. Noting any unusual behavior can provide insights into the mass’s impact, greatly assisting healthcare providers in determining the best course of action.
Key symptoms to note include health history, growth rate of the mass, and any discomfort reported by the child.
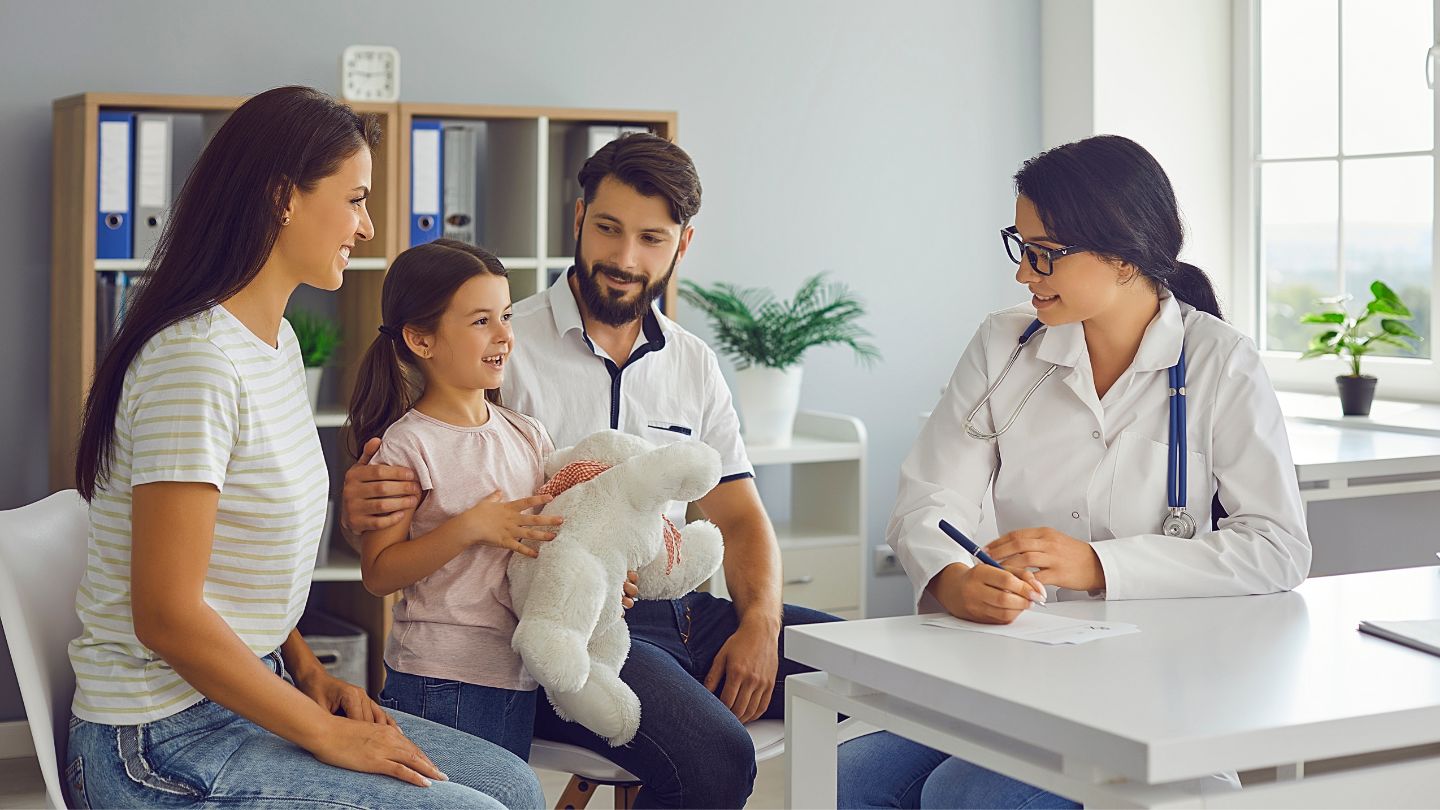
Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare provider if the mass increases in size rapidly or presents unusual symptoms like persistent pain. Notify healthcare providers of any rapid changes in the mass and associated symptoms.
If a large lump starts to rapidly increase in size, it may be a sign of a more serious condition that requires prompt medical evaluation. Ensuring proper medical consultation can be crucial for your child’s health and well-being.
Common Types of Facial Masses and Lesions
Parents should understand the various types of facial masses and lesions, which can range from benign skin growths to congenital lesions, atypical moles, and vascular anomalies. Each type has specific characteristics that influence the treatment approach. Recognizing the type of mass your child has helps in seeking appropriate medical advice and treatment.
Common benign tumors in children include:
- Hemangiomas, which are vascular lesions that typically present shortly after birth.
- Enlarged lymph nodes caused by infections, presenting as palpable masses in the neck or head area.
- Cysts, often developing from remnants of embryonic structures that did not fully obliterate.
The treatment approaches for these masses vary depending on their type and severity.
Benign Skin Growths
Benign skin growths are common in children and can include a variety of types. Dermoid cysts, for example, are non-cancerous growths that often contain hair follicles and sebaceous glands.
Epidermal inclusion cysts typically present as firm, movable lumps beneath the skin’s surface, often resulting from the blockage of hair follicles. These lumps are often called epidermal inclusion cysts, while epidermoid cysts are soft, fatty tumors that are generally painless and can be found anywhere on the body, including the head and neck area.
These benign fibrous growths are generally harmless but should be monitored for any changes in size or appearance, including normal moles.
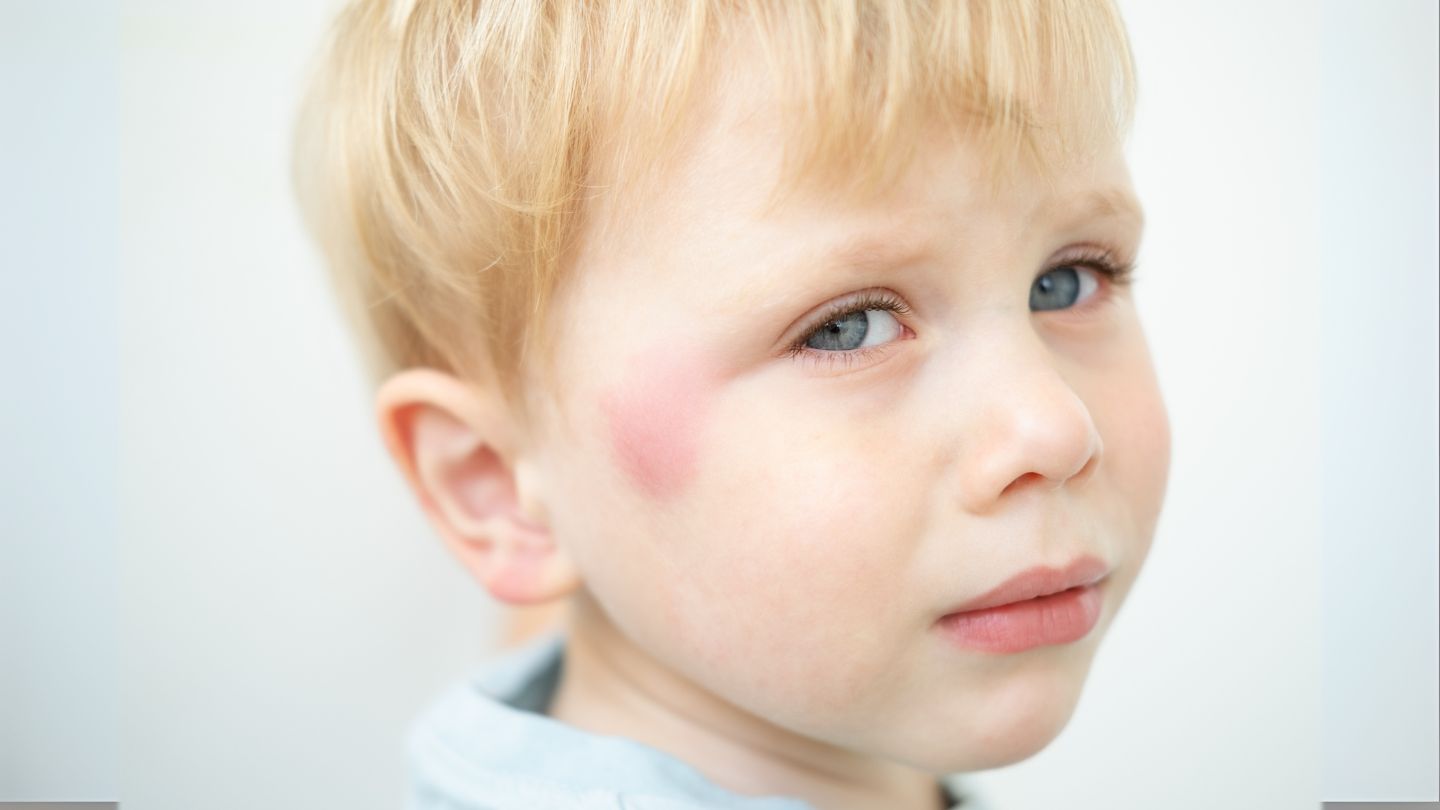
Hemangiomas and Vascular Lesions
Hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors that often appear as red or purple marks on the skin, typically shrink with age, and are considered raised marks caused by blood vessels proliferation. They usually appear shortly after birth, often as flat, red raised marks that grow rapidly in the first few months, sometimes resulting in small blood vessels causing small skin marks caused, including skin colored small skin marks.
The life cycle of hemangiomas includes the following phases:
- Proliferation
- Quiescence
- Involution Most hemangiomas shrink significantly by age five. Understanding their typical appearance and lifecycle can help parents know what to expect and when to seek medical advice.
Congenital Lesions
Congenital lesions like thyroglossal and branchial cysts are present at birth and result from developmental abnormalities during fetal growth. Thyroglossal cysts are typically located in the midline of the neck, arising from remnants of the thyroid gland. Branchial cysts are found along the lateral aspect of the neck and often present as soft, movable lumps.
While these lesions are usually painless, they can become infected, leading to swelling and redness in the affected area, including pyogenic granulomas red.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing facial masses and lesions in children involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests. This thorough approach ensures that the nature of the mass is accurately identified, guiding the appropriate treatment plan.
The diagnostic process can be broken down into several key steps.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will assess the enlargement of lymph nodes, their tenderness, and any warmth in the surrounding skin. Parents should note any associated symptoms like fever or fatigue to aid the doctor in assessment of the lymph node.
Providing a comprehensive family medical history, including occurrences of tumors or head/neck masses, is crucial. Recording the duration of symptoms such as pain or discomfort further aids in diagnosis.
Parents should inform the doctor about any recent injuries like insect bite or cat scratches.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs visualize swollen lymph nodes and assess nearby tissues, helping determine the extent of deeper tissue involvement in the mass or lesion.
These tests provide a detailed internal view, assisting in planning the treatment strategy and ruling out more serious conditions.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves extracting tissue from the mass for microscopic examination to determine if it is benign or malignant. Changes in the mass’s shape or color may indicate a need for further evaluation.
Surgical intervention may be necessary if the mass is suspected to be malignant or causes significant complications. Surgery is often recommended for persistent or symptomatic lumps, or those suspected of being dermoid cysts or other types that may harm surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for facial masses and lesions in children vary depending on the type and severity of the mass. Approaches range from simple observation to medication and surgical removal.
Knowing the different options helps parents make informed decisions about their child’s care.
Observation and Monitoring
In many cases, healthcare providers may recommend observation instead of immediate intervention, particularly for smaller or asymptomatic oval lumps. Lipomas round, which are soft, movable lumps made of fatty tissue and soft tissue cells, are generally harmless and may not require treatment unless they cause discomfort. Fatty deposits can be associated with lipoma changes, but they are typically benign.
Vascular malformations, unlike hemangiomas, are present at birth and do not regress, often requiring ongoing management. Observation over time is recommended to see if the mass changes or resolves on its own.
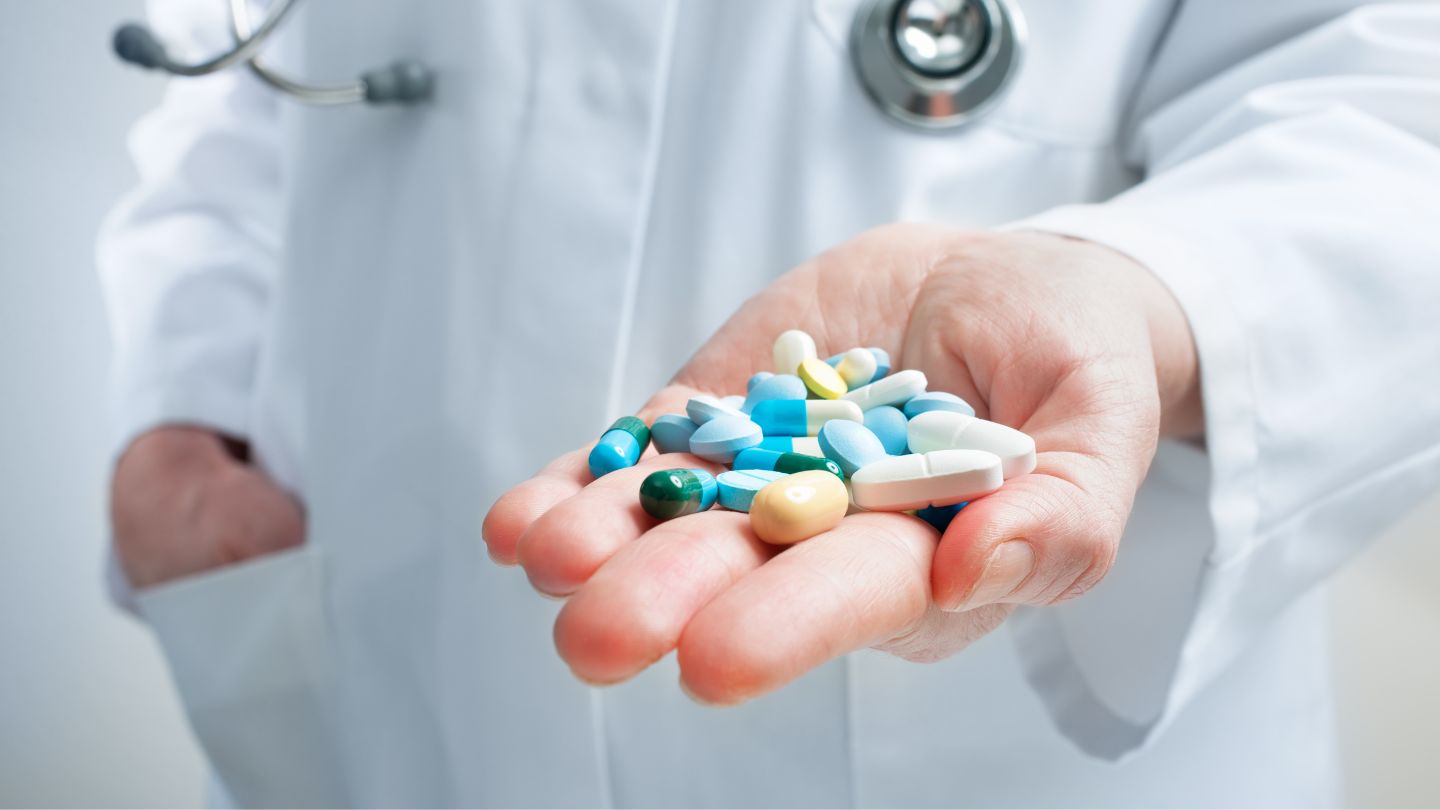
Medications
Corticosteroid drugs may be prescribed to reduce inflammation associated with specific lesions in newborns. These medications can be an important part of the treatment plan, helping alleviate symptoms and manage inflammation associated with certain types of masses.
Surgical Removal
Surgical removal may be necessary when the mass is symptomatic, suspected to be malignant, or causing significant complications. For example, thyroglossal cysts commonly appear as midline neck masses and may require surgically removed if symptomatic.
CT images can guide the surgical procedure when surgery is recommended.
Preventative Measures and Aftercare
Post-treatment care involves several important steps to ensure proper healing and prevent infection. Preventative measures and aftercare are crucial to maintaining your child’s health and avoiding complications.
Avoid Sun Exposure
Protecting children’s skin from sun exposure prevents complications like skin burns and long-term damage. Using broad-spectrum SPF sunscreen shields children from harmful UV rays, significantly reducing the risk of UV damage to their sensitive skin.
Parents should ensure their child wears protective clothing and uses sunscreen, especially in sunny conditions.
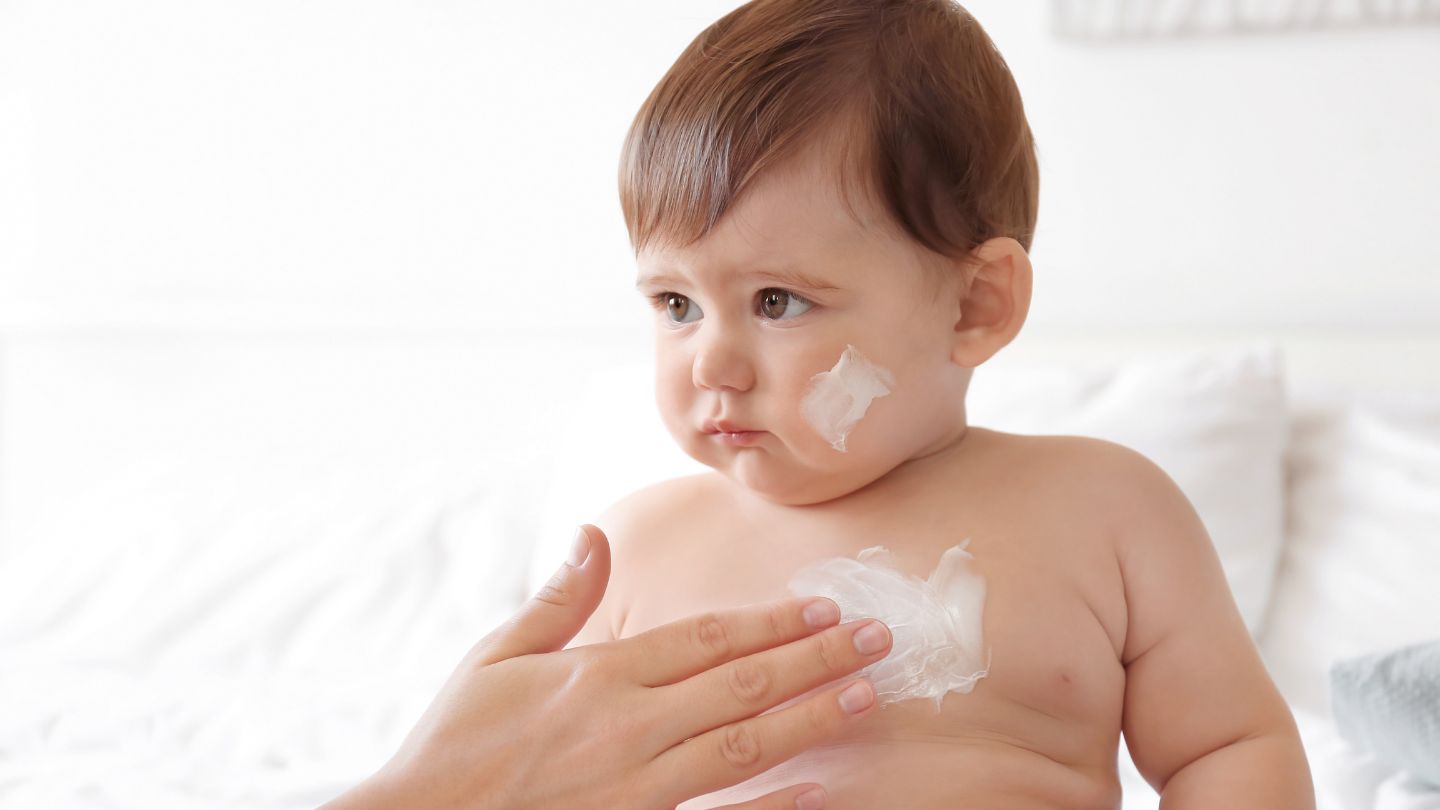
Post-Treatment Care
Keeping the post-treatment area clean and dry promotes healing and prevents infections. Applying prescribed ointments or dressings as directed by a healthcare provider aids in the healing process.
Regularly monitor for signs of a serious infection, such as increased redness or swelling.
Follow-Up Visits
Regular follow-up appointments check for any recurrence of issues and ensure proper healing. These visits allow healthcare providers to assess the healing process and identify any potential recurrence of the lesion.
During these visits, doctors may perform examinations to ensure there are no complications from the treatment.
Final Thoughts
Facial masses and lesions in children require timely recognition, careful monitoring, and professional evaluation to ensure the best outcomes. This blog explores the types of facial masses commonly seen in pediatric patients, steps parents should take when noticing a lesion, and when to seek medical help. It also outlines diagnostic methods such as imaging and biopsy, and reviews treatment options including observation, medication, and surgical removal. Finally, it highlights the importance of post-treatment care and follow-up to prevent complications and promote healing.
At Pediatric Ear Nose and Throat of Atlanta, P.C., families can access expert care for pediatric facial masses treatment in Atlanta. Their team of specialists offers comprehensive evaluations, advanced diagnostics, and customized treatment plans to ensure each child receives the attention and care they need for optimal health and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if I notice a mass on my child’s face?
If you notice a mass on your child’s face, it is important to observe it for any changes in size, shape, or color and to document any symptoms. Seek medical advice promptly if you have concerns or if the mass grows rapidly.
Are facial masses in children usually cancerous?
Facial masses in children are typically benign; however, it is crucial to monitor any new or changing lesions and seek evaluation from a healthcare provider.
What are common types of benign skin growths in children?
Common benign skin growths in children include dermoid cysts, epidermal inclusion cysts, and lipomas, which are generally harmless but should be monitored for any changes.
How are facial masses diagnosed?
Facial masses are diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs, and, when necessary, a biopsy to analyze the tissue. This comprehensive approach ensures accurate identification and assessment of the mass.
What treatment options are available for facial masses in children?
Facial masses in children can be treated through observation, corticosteroid medications, or surgical removal, tailored to the specific type and severity of the mass. Seeking medical advice is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment plan.